Any text structure can be represented using Markov Chain states and transition probabilities, for the sake of simplicity I’ll not use probabilities to describe the state transitions, I’ll use only true or false, saying only that this transition is possible or not (100% or 0%).
A Markov Chain in this simple form can be formulated as a set of possible states, lets say 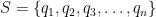 as well a dictionary-like data structure in the form of
as well a dictionary-like data structure in the form of  representing the possible transition states, but let’s put an example text on it to make it clear:
representing the possible transition states, but let’s put an example text on it to make it clear:
the white rabbit and the white fox
Then the possible states of this text are  , and the dictionary structure should be:
, and the dictionary structure should be:


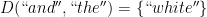

These transition rules can be incrementally updated. Note that these rules represent the structure of the text and not the text by itself; when updated for instance, with a whole book, it captures the profile of the writer, the characteristics often used by the author, even more enforced when incrementally updated with more than one book of the same author.
I implemented a simple tool using Python and NLTK (just to parse and tokenize the text) that can be used to read an input text and incrementally update a Markov Chain data structure in a way to be reused later in order check similarity with another text.
The most interesting part of these chain is that they also offer a property present in Bloom Filters: false positives are possible but not false negatives. In terms of our implementation and formulation, that property means that if we update a chain with the text of two books from Lewis Carroll, there would be (and of course, is a very low probability) another author (that the chain was not trained with their books) who can have the same chain, creating in this way a false positive, because the same chain from Lewis Carroll books could have the same chain of another different book, but you should note that is almost impossible (actually this fact would be very strange, since the authors style and words used are required to be almost the same) to find books from different authors who share the same chain.
You should note that we can also compare different chains in order to measure similarity between two authors/book profiles. This comparison is done by searching a previous trained chain (with the same author books or not) for the entries of the current chain in order to match the same structure of the chains and then calculate a ratio between the matches found and the total rules of the chain we are checking.
But hey, that’s a lot of blah blah blah and nothing of code, let’s see it in practice. Here is the help of the implemented tool (I created a repository in GitHub if you’re interested in the source-code):
$ python -m pymarksim.markov --help
pymarksim v.0.1
By Christian S. Perone <christian.perone@gmail.com>
https://blog.christianperone.com
Type --help parameter for help.
Options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-d DUMP_FILE, --df=DUMP_FILE
Pickle object file ex. pickle.db
-i INPUT_TEXT, --input-text=INPUT_TEXT
Input text
-m MODE, --mode=MODE Mode of operation: train, check
-c COMPRESS_LEVEL, --compress-level=COMPRESS_LEVEL
The gzip compression level, default is 9 (max).
So let’s train a chain using the “Alice Adventure’s in Wonderland” book (alice_adventures.txt) from Lewis Carroll (took from the Project Gutenberg):
$ python -m pymarksim.markov -d lewis.db -i alice_adventures.txt -m train
pymarksim v.0.1
By Christian S. Perone <christian.perone@gmail.com>
https://blog.christianperone.com
Type --help parameter for help.
File lewis.db not found, creating a new one...
Updating...
Done !
Here the tool created the file lewis.db which is the chain in a Python dictionary structure (I’ve used the cPickle module to serialize it and gzip compression). Now let’s check how close is this chain from the original text book:
$ python -m pymarksim.markov -d lewis.db -i alice_adventures.txt -m check
pymarksim v.0.1
By Christian S. Perone <christian.perone@gmail.com>
https://blog.christianperone.com
Type --help parameter for help.
File lewis.db found, loading...
Checking...
Match 100.00 %
As you can see, we have a perfect match between the chain and the text book. Now comes the interesting part, let’s check an unrelated book with this chain trained with the Alice Adventure’s in Wonderland, for this, I took the book “The Adventures of Sherlock Holmes” (doyle.txt) from Sir Arthur Conan Doyle (also from the Project Gutenberg):
$ python -m pymarksim.markov -d lewis.db -i doyle.txt -m check
pymarksim v.0.1
By Christian S. Perone <christian.perone@gmail.com>
https://blog.christianperone.com
Type --help parameter for help.
File lewis.db found, loading...
Checking...
Match 7.14 %
See that now the match of the chain from Sherlock Holmes with the Alice Adventure’s is now 7.14%, remember that a perfect match is 100.00 % !
Let’s check now this chain trained only with the Alice Adventure’s in Wonderland of Lewis Carroll with another book from the same author, called “Through the looking-glass” (looking-glass.txt):
$ python -m pymarksim.markov -d lewis.db -i looking-glass.txt -m check
pymarksim v.0.1
By Christian S. Perone <christian.perone@gmail.com>
https://blog.christianperone.com
Type --help parameter for help.
File lewis.db found, loading...
Checking...
Match 25.93 %
See that now we have a match of 25.93% ! Let’s check with a more related book also from Lewis Carroll, called “Alice Adventure’s Under Ground” (underground.txt):
$ python -m pymarksim.markov -d lewis.db -i underground.txt -m check
pymarksim v.0.1
By Christian S. Perone <christian.perone@gmail.com>
https://blog.christianperone.com
Type --help parameter for help.
File lewis.db found, loading...
Checking...
Match 57.84 %
That’s very related don’t you think ?
I hope you liked it, Markov Chains are a very powerful way to capture system processes, and can be used in ways we usually do not expect.
“So many out-of-the-way things had happened lately, that Alice had begun to think that very few things indeed were really impossible.” – Alice Adventure’s in Wonderland
 RSS Feeds
RSS Feeds Newsletters
Newsletters Bookmark
Bookmark